Mar 19, 2018
Robust wifi-based indoor localization
Physical Sciences, IT and Communication
- Smartphone-based indoor-navigation
- Highly precise localization (below 1m)
- Robustness to environmental changes
Your contact
Stephan Ottmar
- E-Mail:
- sottmar@baypat.de
- Phone:
- +49 (0) 89 5480177 - 37
- Reference Number:
- B77076
Factsheet
Download Tech Offer (PDF)Challenge
Indoor localization and navigation systems are becoming more and more popular, based on their po-tential of quickly and efficiently guiding a user through a large building (airport, mall and similar). The basic motivation for developing such systems is that conventional outdoor navigation systems (GPS) are inefficient in closed environments. Very often, indoor navigation systems are based on the detection of WiFi-signals. This is advantageous, because most buildings are already equipped with WiFi-antennas. Additionally, a WiFi-system can identify the user though the MAC-Address of its mobile device. The big-gest disadvantage of localization systems based on WiFi consists of the poor spatial resolution (usually 1-10 m). An additional problem in WiFi-based indoor localization is the loss of precision when a user is localized in a dynamic environment. Indoor environment are subjected to quick and unpredictable changes (people or objects in a corridor, closed and open doors or windows), which can dramatically modify the reflection path of the WiFi-signal and consequently the efficiency of the localization.
Innovation
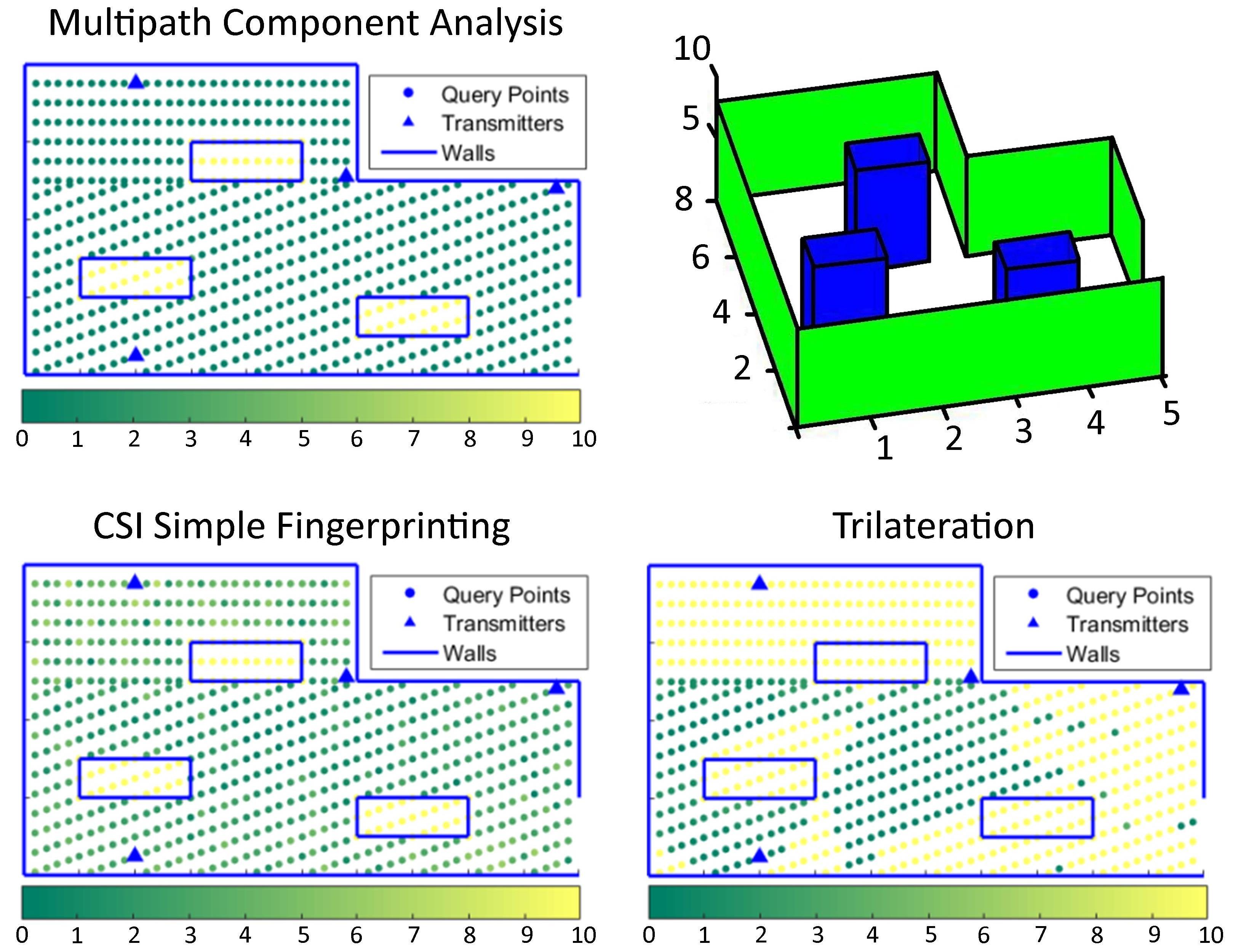
The present invention focuses on improving the spatial resolution achievable with a WiFi-based in-door localization system and addressing the problem of the robustness to changes in the surrounding environment. The invention consists of a localization algorithm based on a Multipath Component Ana-lysis (MCA). The localization procedure consists of an off-line phase in which a multipath delay profile (MPD) is measured for every position at which a receiver is located. The receiver could be a movable detector station driven through the building. In the on-line phase, one MPD is measured at the position of the user and a similarity metric is computed based on the extraction of the multipath components. This algorithm has the following advantages with respect to the state of the art:
- It allows for the localization of a user inside a building with high precision (up to below 1m);
- The localization is extremely robust to changes in the environment (movable objects, variable amount of people in the building), the off-line phase does not need to be repeated frequently.
Commercial Opportunities
The algorithm can be applied to all indoor navigation applications based on WiFi-systems.
Development Status
References
-
Reference:
2017 International Conference on Indoor Positioning and Indoor Localization (IPIN), Semptermber 2017.