Oct 16, 2020
Designed Chemokine-Selective Peptides in the Fight Against Atherosclerosis and Inflammation
Life Sciences, Cardiovascular Disease
- Novel class of therapeutics for atherosclerotic plaques
- Soluble peptide-based mimics of the CXCR4 receptor
- High potency and target specificity
Your contact
Dr. M. Charlotte Hemmer
- E-Mail:
- chemmer@baypat.de
- Phone:
- +49 (0) 89 5480177 - 29
- Reference Number:
- B80034
Factsheet
Download Tech Offer (PDF)Challenge
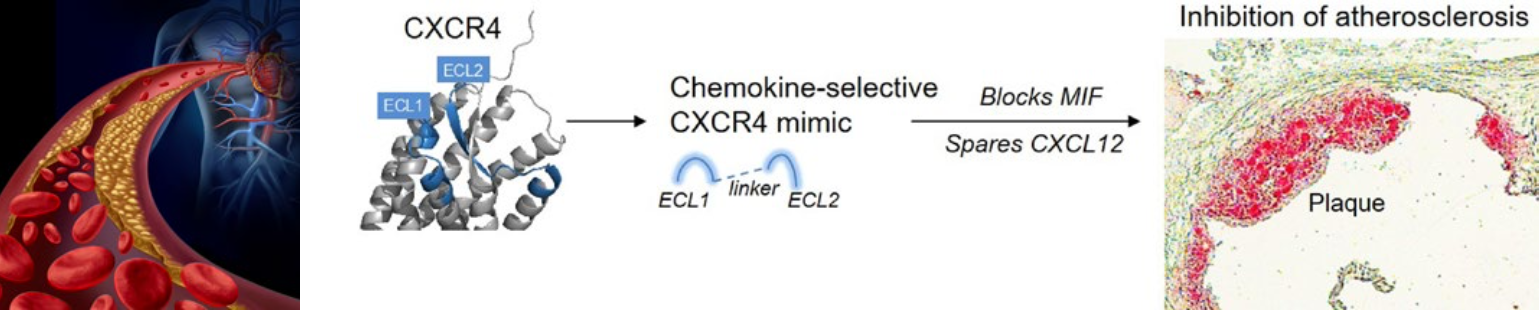
In coronary heart diseases, a progressive narrowing of blood vessels results in a life-threatening interruption of the blood flow to the heart. Atherosclerosis is considered the main underlying pathology. Here, accumulating lipids result in the thickening and hardening of blood vessels as plaques. In recent years, atherosclerosis has also been linked toinflammatory processes orchestrated bycytokines and chemokines. By acting on their target cells via specific surface receptors, these small signal proteins drive the migration of immune cells in tissue and bloodstream to sites of infection or sterile inflammatory foci. Due to their strong involvement in different inflammatory processes, they represent promising therapeutic targets. One key signaling hub in atherosclerotic pathogenesis is the chemokine receptor CXCR4. CXCR4 is ubiquitously expressed, but has particularly critical roles in atherosclerosis when expressed on leukocytes and aortic endothelial cells. It also exerts context-dependent functionsdepending on the engaged ligand. Binding the classical chemokine ligand CXCL12 leads to important atheroprotectiveeffects, whereas activation by the atypical chemokine ligand MIF, also known as a potent pro-inflammatory cytokine, promotes atherosclerosis. Despite the unmet need for effective anti-inflammatory therapeutic approaches directed against cytokine- and chemokine-mediated pathways, selectively targeting a specific chemokine-receptor axis has proven to be challenging.
Innovation
Our novel approach involves soluble peptide-based mimics of the CXCR4 receptor. These mimics show potent chemokine-selectivity and differentiate between MIF and CXCL12. By localizing to atherosclerotic plaques, they inhibit MIF-mediated leukocyte recruitment and arterial adhesion¹. Importantly, they do not affect the atheroprotective function of CXCL12.
Commercial Opportunities
Our selective CXCR4 mimics represent a novel class of therapeutics for the treatment of atherosclerotic plaques and related inflammatory diseases:
- cost-effective production by routine solid phase peptide synthesis methodology
- small-medium-sized peptides (<30 residues)
- high potency andtarget specificity and good proteolytic stability
- Structural template for small molecule design with anti-atherosclerotic function
- IP covers extension of approach to other chemokine receptors and/or different selectivity
Development Status
Proof-of-concept in in vivoApoe−/− mouse model, human plasma, and patients’ biopsy samples.
References
-
1
doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-19764-z