Apr 17, 2023
New catalysts for the production of superior PHB
Life Sciences, Chemical Process
- Biocompatible and biodegradable plastic with superior material properties compared to bacterial PHB
- Cost-effective production via ring opening polymerization of ß‐butyrolactone
- Thermomechanical properties similar to petrochemical PP, material suitable for melt processing
Your contact
Dr. Rebecca Kohler
- E-Mail:
- rkohler@baypat.de
- Phone:
- +49 (0) 89 5480177 - 33
- Reference Number:
- B82063
Factsheet
Download Tech Offer (PDF)Challenge
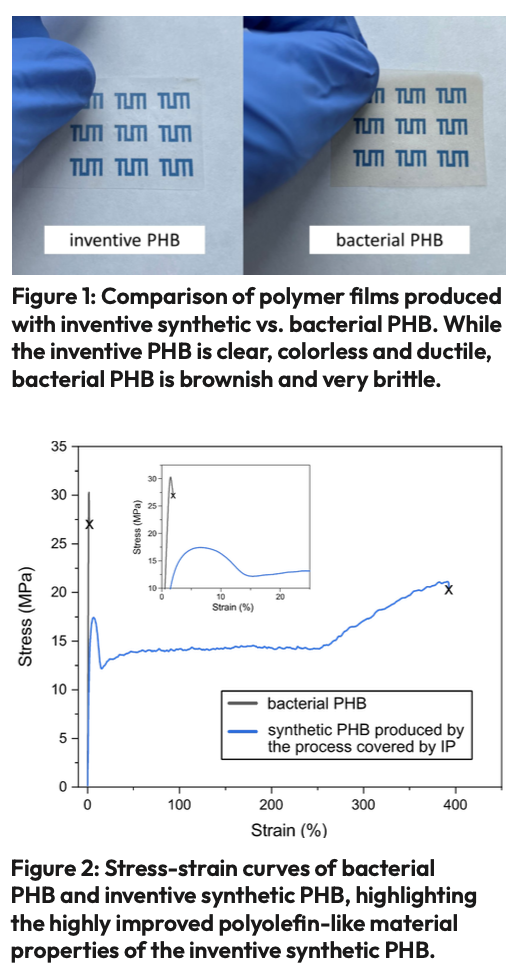
Poly(3‐hydroxybutyrate) is a biocompatible and biodegradable thermoplastic polyester that can be produced from renewable starting materials. However, pure isotactic PHB produced by fermentation processes has a very limited application potential since it is very brittle and difficult to process. Improved material characteristics similar to those of well-established petrochemical plastics such as polypropylene are essential for competitiveness of PHB bioplastics.
Innovation
The inventive PHB is, in comparison to bacterial PHB, favorably characterized by a high ductility and a lowered meltingpoint enabling melt processing. It is clear and colorless, so that attractive optics can be achieved including transparency and light or bright colors after dyeing. The inventive PHB also lends itself to chemical recycling into the monomers, enabling circular polymer economy approaches. Based on its properties and cost-effectiveness the inventive PHB is ideal for packaging solutions and as a substitute for e.g. polyolefins in various applications.
Commercial Opportunities
Cost-effective, biocompatible and biodegradable PHB plastic, especially suited for packaging for e.g. food or medical single-use items. The inventive PHB is transparent and colourless and can be stained in bright colours.
Development Status
Technology Readiness Level 4